
Magento 2 Customer Tax Class: Types and Working
Ready to streamline your tax configurations and simplify tax management? Magento 2 customer tax class helps manage tax rules based on customer groups. It ensures accurate tax calculations.
In this tutorial, we will explore the types and workings of Magento 2 customer tax class.
Key Takeaways
-
Magento 2 customer tax classes for shipping impact tax calculations.
-
Create and assign custom customer tax classes for different customer groups.
-
Rules for tax work with both customers and products for accurate tax rates.
-
Configure tax zones, rules, and automation in Magento 2.
-
Stay compliant with tax laws and manage international tax scenarios.
-
Difference Between Product and Customer Tax Classes in Magento 2
-
Best Practices for Managing Tax Classes and Rules in Magento 2
What is Magento 2 Customer Tax Class?
Magento 2 customer tax class determines how taxes are applied to customers based on their group classification.
Tax classes categorize customers into groups for tax calculation purposes. They ensure accurate tax rates depending on factors like:
-
Location
-
Business Type
-
Exemptions
These tax classes include tax classes for products and tax rules to ensure the proper calculation of taxes. Assigning customers to the right tax class helps manage tax compliance. This is especially true when dealing with various:
-
Customer groups
-
Locations
-
Tax-exempt organizations
Different Magento 2 Customer Tax Classes
1. Retail Customer
-
It is the default customer tax class. It is assigned to individual consumers who make personal purchases from an online store.
-
These customers typically pay standard tax rates based on their location.
-
It ensures that individual buyers are taxed according to the general sales tax laws applicable in the region.
2. Wholesale Customer
-
It is designed for businesses purchasing products in bulk or at wholesale prices.
-
Wholesale customers often have different tax obligations compared to retail buyers.
-
For example, they may benefit from reduced tax rates or exemptions in certain regions.
-
The tax class allows online stores to adjust tax calculations for B2B transactions. It is ideal for stores serving both B2C and B2B customers.
3. Tax-Exempt Customer
-
The class is used for customers or organizations that are exempt from paying taxes, such as:
1. Non-profits
2. Government agencies
3. Tax-exempt businesses
-
Store owners can assign this tax class to individual customers or entire customer groups. They ensure that taxes are not applied during checkout.
-
Tax-exempt status may vary by region, so assigning customers to this class ensures compliance with local tax laws.
4. Custom Tax Classes
-
Magento 2 allows store owners to create custom customer tax classes. It accommodates specific business needs or regional tax regulations.
-
For example, a store operating in multiple countries with varying tax rules might create separate tax classes for:
1. International customers
2. Non-residents
3. Customers from tax-free zones
-
The flexibility ensures that the store can adapt to unique tax scenarios. They can apply the appropriate rates based on the customer’s profile.
How Magento 2 Customer Tax Classes Work?
1. Integration with Product Tax Classes
-
Magento 2 uses a combination of customer tax classes and product classes. It helps determine how much tax is applied to a transaction.
-
The customer tax class defines the buyer's tax status. The product class for tax categorizes the goods or services being purchased.
-
Some products might be exempt from sales tax in certain jurisdictions, while others are taxable.
2. Tax Rule Application
-
Once both customer and product classes are determined, Magento 2 applies tax rules to calculate the correct tax rate.
-
Rules for tax consider the:
1. Customer’s location (via shipping address)
2. Product’s tax category
3. Customer’s tax class to arrive at the appropriate tax amount
-
It ensures compliance with local, regional, or international tax regulations.
3. Handling of Multiple Customer Groups
-
Magento 2’s flexible structure allows for the creation of multiple customer tax classes to cater to various scenarios.
-
A store owner can set up a specific tax class for international customers. The tax can be adjusted for different tax rules in Magento 2. It is based on whether the sale involves domestic or cross-border transactions.
-
Special rates can be assigned to certain customer groups, such as employees or VIP members. They may benefit from specific tax treatments.
4. Customization for Specific Needs
-
Magento 2 provides the flexibility to create custom tax classes for special circumstances.
-
It is particularly useful for businesses operating in multiple regions with diverse tax requirements.
-
Custom tax classes help accommodate different tax rates and rules. The tax system becomes adaptable to changing business conditions.
How to Create and Assign Customer Tax Classes in Magento 2?
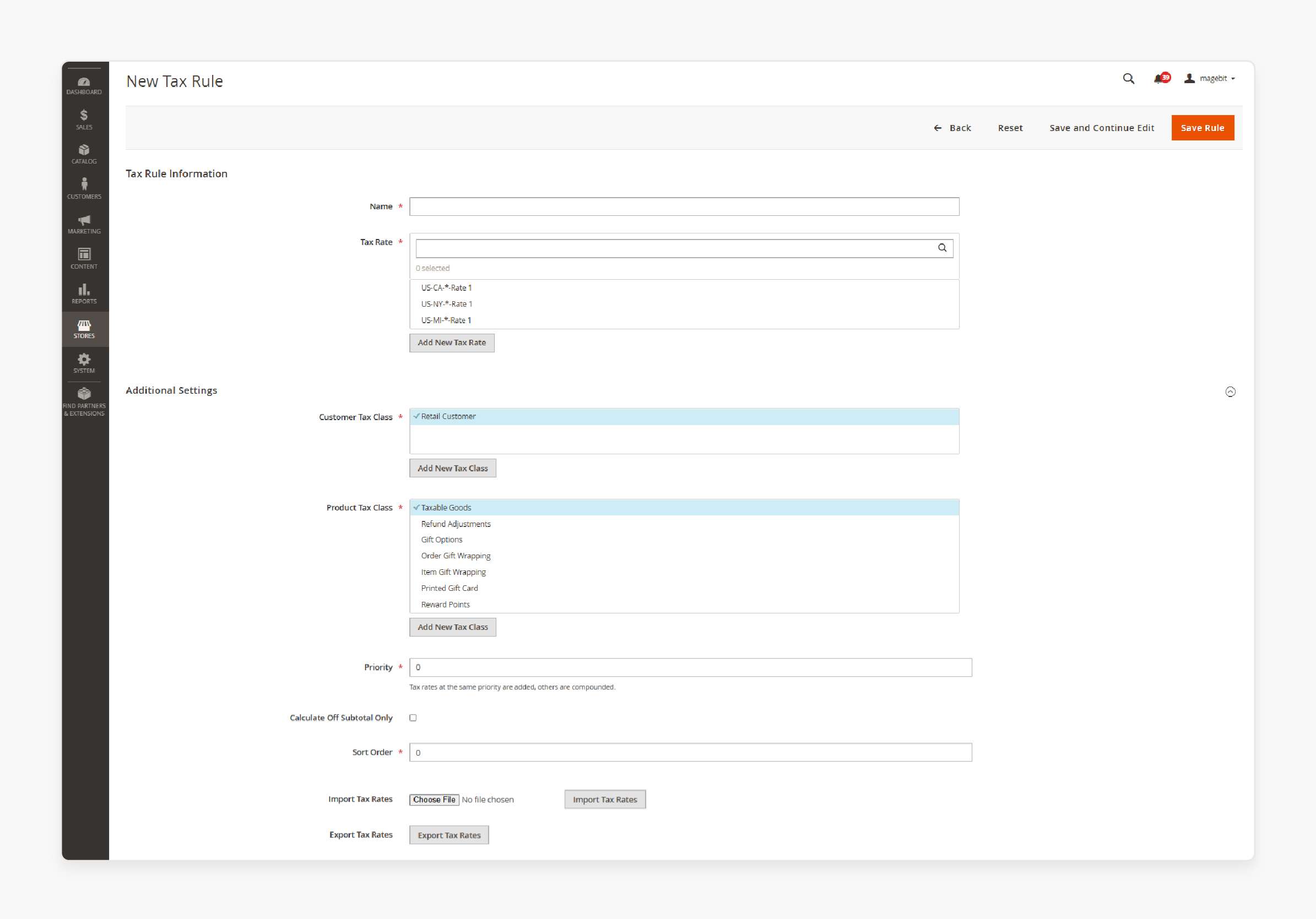
Step 1: Access the Additional Settings section
1. Log in to your Magento admin panel.
2. From the sidebar, go to Stores > Taxes > Tax Rules.
3. Click Add New Tax Rule and locate the Additional Settings section. Click to expand it.
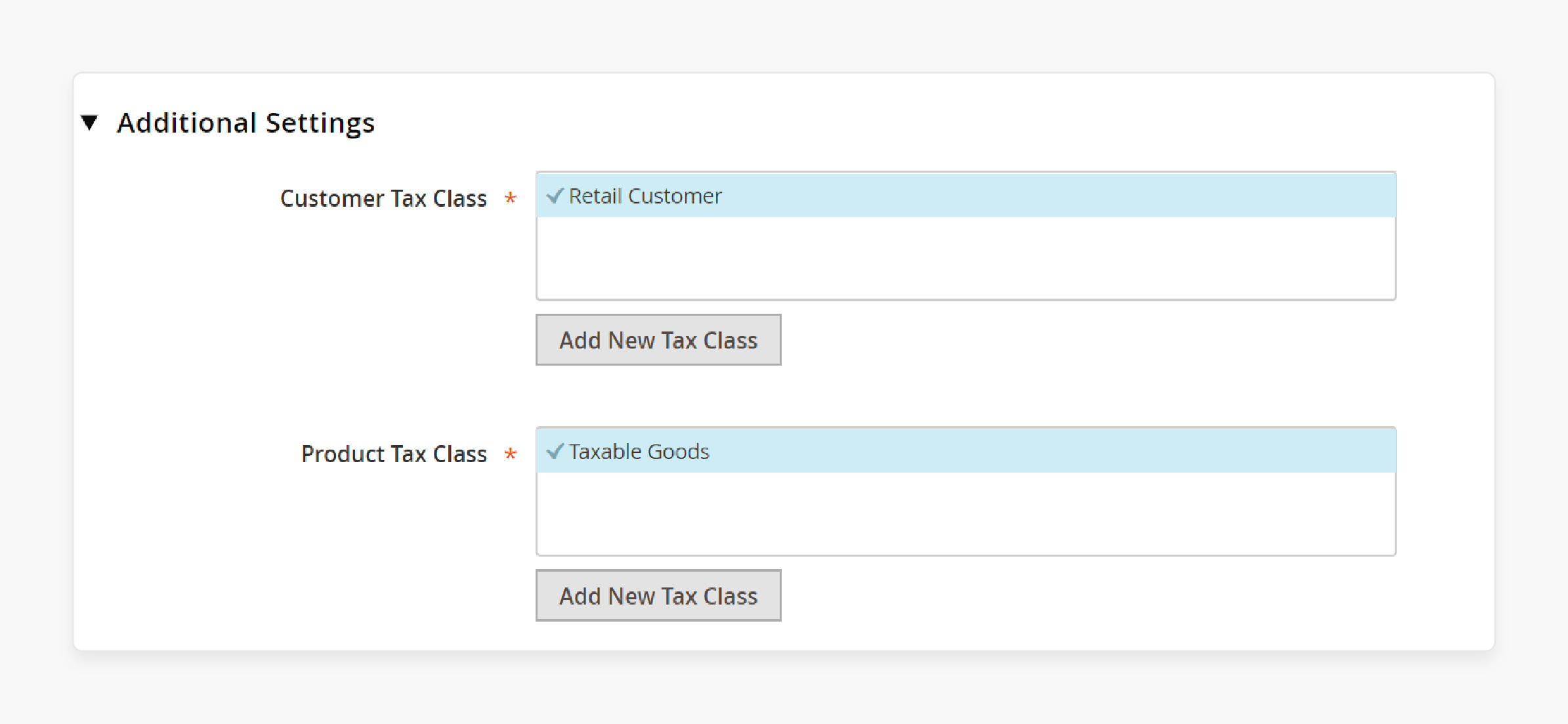
Step 2: Add a new Customer Tax Class
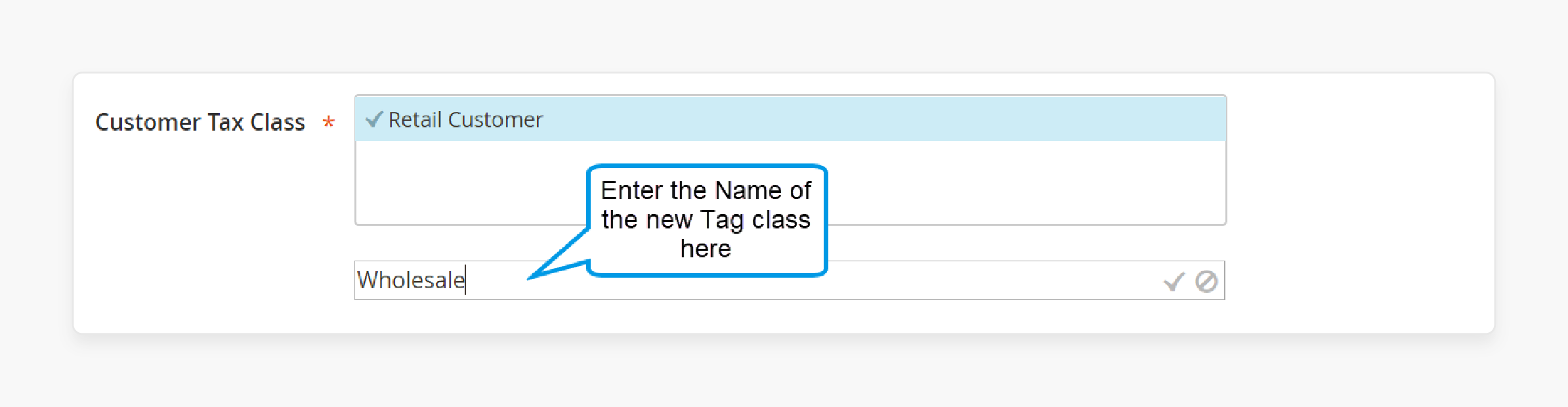
1. Under Customer Tax Class, click Add New Tax Class.
-
By default, "Retail Customer" is listed, but you can add a new one. For example, enter “Wholesale” in the textbox.
-
Check the box to save this new class under your customer tax classes.
Step 3: Add a new Product Tax Class
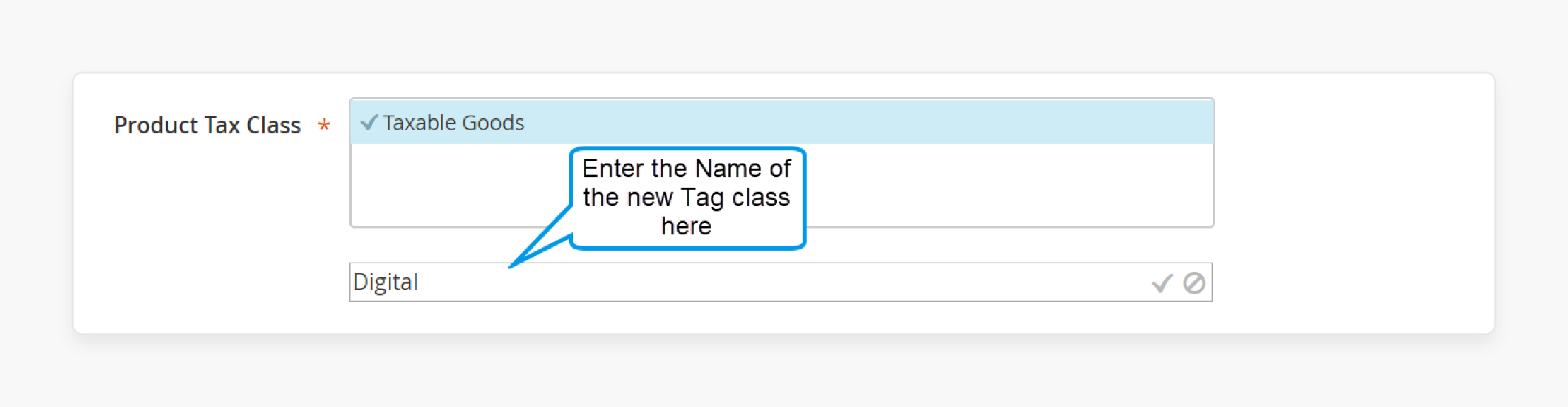
1. Under Product Tax Class, click Add New Tax Class.
2. A textbox will appear. Enter the name of your new class, like “Digital”.
3. Be sure to check the box to add it to the list of product classes.
Step 4: Complete
Once all tax classes are added, click Back to return to the Tax Rules grid.
Difference Between Product and Customer Tax Classes in Magento 2
| Criteria | Product Tax Class | Customer Tax Class |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Purpose | It defines the taxability of products or services and applies specific tax rates. | It classifies customers into tax groups. These are based on their status for tax calculation. |
| 2. Application | It is assigned to individual products. It determines whether they are taxable or non-taxable. | It is assigned to customer groups or individual customers. It specifies how they are taxed |
| 3. Examples | Taxable Goods, Non-Taxable Goods, Reduced Rate Goods | Retail Customer, Wholesale Customer, Tax-Exempt Customer |
| 4. Focus | It focuses on how products are taxed based on their category and location. | It focuses on how customers are taxed based on their group or tax-exempt status. |
| 5. Relation to Checkout | The tax class of the product influences the total tax amount on the order. | The customer's tax class affects how taxes are applied or exempted in the final calculation. |
| 6. Usage Scenario | Physical items like clothing or electronics are taxed based on product class. | A tax-exempt customer won’t be charged tax at checkout. A retail customer will be taxed based on location. |
| 7. Customization | Merchants can create custom product classes for special products or services. | Merchants can create custom customer tax classes for specific groups, like international clients. |
| 8. How It Works with Magento 2 Tax Rules | Rules for tax combine product classes with customer tax classes. It applies the right rate for both the product and the customer class. | Rules for tax assess customer groups and apply the corresponding tax rate. It is based on customer and product classes. |
Best Practices for Managing Tax Classes and Rules in Magento 2
1. Configure Tax Zones and Rates
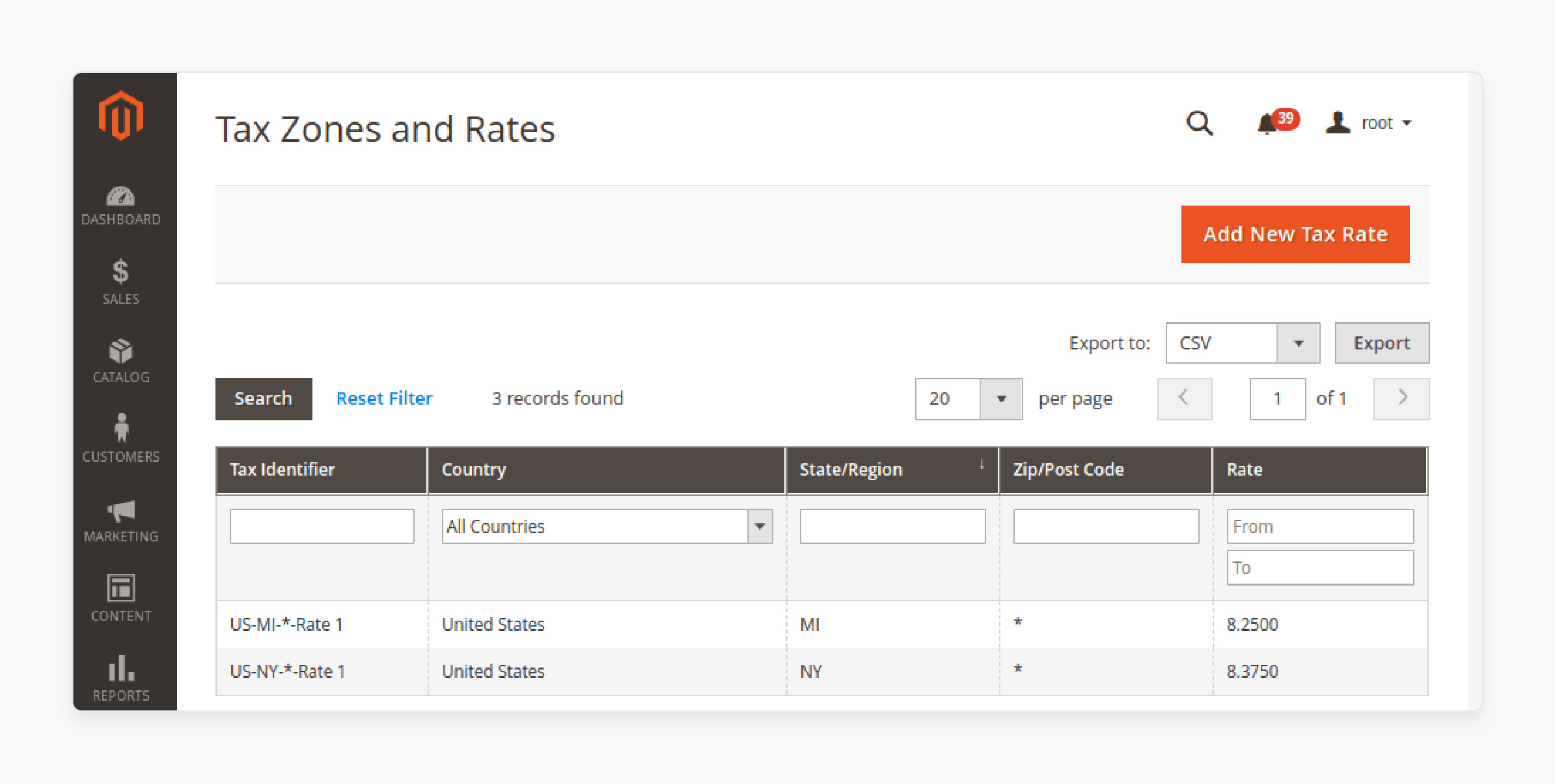
Set up specific tax zones and rates based on your business location and where your customers reside. Ensure that:
-
You include all applicable jurisdictions (local, state, federal, etc.).
-
You regularly update tax rates in Magento to reflect changes in tax laws.
-
For international sales, ensure that VAT (Value-Added Tax) rates are accurately configured for the countries you sell in.
2. Use Default Magento Tax Rules
Magento provides a set of default tax rules that fit most common tax scenarios. Customize these rules based on the specific needs of your business. When setting up custom rules, consider:
-
Prioritizing the rules to avoid overlap.
-
Ensuring that product-specific rules for tax are always correctly assigned. It is mainly for exempt items or special tax rates.
3. Automate Tax Calculations
Use a tax calculation service to stay compliant and reduce the manual work of updating tax rates. Tools like Avalara or TaxJar can be integrated with Magento 2 to:
-
Automatically fetch and apply tax rates based on customer location.
-
Handle complex tax scenarios, such as nexus laws or sales tax, across multiple states or countries.
4. Ensure Tax Configuration for Shipping
Shipping costs may or may not be taxable, depending on local regulations. When configuring tax rules:
-
Assign tax rules to shipping methods to ensure that they are taxed correctly if required by law.
-
Always check whether shipping tax settings align with the regions where you're shipping products.
5. Test Tax Rules Regularly
After configuring tax rules, test the system by placing test orders with different customer profiles and locations. Ensure that:
-
Tax is applied correctly to the products, shipping, and the final total.
-
Tax displays correctly during Magento checkout, and customers are not over or undercharged.
6. Stay Compliant with Tax Reports
Magento 2 provides tax reports under the "Reports" section, which can help you:
-
Track tax amounts collected across different locations and time periods.
-
Export tax data for filing tax returns and ensuring compliance with your local tax authorities.
7. Monitor Updates to Tax Laws
Tax laws change frequently, especially for businesses selling across multiple states or countries. Set up a process to:
-
Regularly review tax laws in the regions where you operate.
-
Update your Magento 2 tax rates and rules accordingly to avoid compliance issues.
8. Use Customer Groups for B2B and B2C Taxation
For B2B sales, consider using customer groups to manage different tax scenarios. For example:
-
Tax exemptions can be applied to specific B2B customer groups.
-
B2C customers can continue to be taxed according to the default tax class for products and rules.
FAQs
1. How do I add a new tax rate in Magento 2?
To add a new tax rate, navigate to Stores > Taxes > Tax Zones and Rates. Click Add New Tax Rate, then enter the required details like country, region, and rate percentage. Save the changes to apply the rate in your store.
2. What is the default tax destination in Magento 2?
The default tax destination is set based on the customer’s shipping address. Magento 2 uses this address to calculate the appropriate tax for the order. It ensures compliance with local tax laws.
3. How can I view a full tax summary in Magento 2?
You can generate a full tax summary by going to Reports > Sales > Tax. The report provides a detailed breakdown of all collected taxes. It includes the customer group and tax class for accurate reporting and filing.
4. What happens if the tax calculation method returns a zero tax subtotal?
If the tax calculation method results in a zero tax subtotal, it could be due to tax-exempt customers or zero-rated products. Ensure that the correct tax classes and rates are applied to avoid calculation errors.
Summary
Magento 2 customer tax class allows businesses to categorize customers into specific tax groups for accurate tax calculations. The tutorial uncovers the different tax classes, including:
-
Retail customers pay standard tax rates based on their location.
-
Wholesale customers may benefit from reduced rates or exemptions.
-
Tax-exempt customers include non-profits and government agencies.
-
Magento 2 allows the creation of custom tax classes for unique tax scenarios.
Looking to streamline your tax setup with Magento 2 customer tax classes? Ensure smooth tax compliance with managed Magento hosting.









