
Fix Magento 404 Error And Enhance Conversion
Did you know 73% of users won’t return after a broken link? Magento 404 error can frustrate visitors and even cost you sales.
In this article, we will explore the types, causes, and best practices for Magento 404 errors.
Key Takeaways
-
404 errors can block customers or restrict admin access.
-
404 errors impact SEO and performance.
-
Follow best practices to prevent broken links.
-
Fix errors with 301 redirects and store settings.
-
Keep your Magento store error-free and user-friendly.
What are Magento 404 Errors?
A Magento 404 error occurs when a webpage is not found on the server. It happens when URLs are incorrect, pages are deleted, or configurations are faulty.
Magento 404 can appear on the front end. It affects customers or blocks backend access in the admin panel. Common causes of the error include:
-
Missing redirects
-
Cache issues
-
Incorrect base URLs
-
Extension conflicts
These errors hurt SEO and sales by preventing visitors from accessing important pages. Fixing them involves clearing the cache and checking store settings. Regular maintenance helps prevent broken links and ensures smooth site performance.
5 Types of Magento 404 Errors
| Types | Explanation | Common Causes | Fixes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Frontend 404 Errors | These errors occur when customers visit pages that no longer exist or have incorrect URLs. These include product pages, categories, and CMS. | If a product, category, or CMS page is deleted or moved, no 301 redirects are set up. Magento returns a 404 error. If a page links to a non-existent URL, users see a 404 error. It often happens after site restructuring. If the cache is not refreshed or indexing is not updated, old URLs may still be stored. It leads to 404 errors. | Set up 301 redirects in Magento for moved or deleted pages. Clear the cache and reindex Magento data. Check and update URL rewrites in the admin panel. |
| 2. Admin Panel 404 Errors | Magento admins may experience 404 errors when accessing certain backend pages. It occurs after updates, extensions, and misconfigurations. | Changing the admin URL without updating the Magento configuration can cause access issues. Magento may block access with a 404 error if an admin user lacks proper permissions. Some third-party modules interfere with admin functionality. It leads to missing admin pages. | Clear cache and session storage using SSH. Check user roles and permissions in the admin panel. Disable conflicting extensions using SSH. |
| 3. Storefront 404 Errors Due to Base URL Issues | When the Magento store URL is incorrect, all pages may return 404 errors. It often occurs after migrations, domain changes, and SSL updates. | If Magento still points to an old domain, users will see 404 errors. A store set to force HTTPS may return errors if SSL is not properly configured. Incorrect settings in Apache or Nginx may prevent Magento from serving pages. | Update the base URL via SSH. Verify SSL settings and force HTTPS only if SSL is installed. Check server configuration files. |
| 4. 404 Errors from Custom Modules & Extensions | Third-party Magento extensions sometimes modify URLs or interfere with store functionality. It causes broken links. | Custom extensions may generate URLs that don't exist. If an extension is uninstalled but its URLs are still in use, it will return 404 errors. Some modules override Magento’s default routing, leading to broken pages. | Check installed modules and disable conflicting ones. Regenerate URL rewrites and check for missing routes in routes.xml. Use 301 redirects for any outdated extension-generated URLs. |
| 5. .htaccess and Server Configuration 404 Errors | The .htaccess file and web server settings control URL rewriting. Misconfigurations can block access to Magento pages. | Magento URLs won't resolve correctly if this file is missing or incorrectly edited. Some setups may block Magento’s index.php or remove important directives. Permissions or mod_rewrite settings may be incorrect. | Restore the default .htaccess file from Magento. Enable Apache’s mod_rewrite. For Nginx, check the nginx.conf file and ensure rewrite rules are correctly set. |
7 Common Causes of Magento 404 Errors
| Common Causes | Explanation | Reasons | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Incorrect URL Rewrites | Magento uses URL rewrites to create SEO-friendly URLs. If these are misconfigured, it can result in broken links, leading to 404 errors. | Old URL rewrites pointing to non-existent pages. Conflicts due to changes in product/category names. Custom rewrite rules that overwrite Magento’s default behavior. | Navigate to Marketing > SEO & Search > URL Rewrites in Magento Admin. Remove or update outdated URL rewrites. Refresh the rewrite index. |
| 2. Missing or Corrupt .htaccess File | Magento relies on the .htaccess file to manage URL structures and redirects. If this file is missing or modified incorrectly, 404 errors can occur. | Accidental deletion or modification of .htaccess. Corrupt .htaccess after updates or server changes. | Check if .htaccess exists in the Magento root directory. Restore it by downloading the default Magento .htaccess file. Reset file permissions. |
| 3. Disabled or Incorrectly Configured Modules | Magento modules control different functionalities, including URL handling. If a required module is disabled, related pages may return 404 errors. | Manually disabling modules without checking dependencies. Module conflicts after an update. | Check the status of modules. Enable missing modules if necessary. |
| 4. Cache and Index Issues | Magento uses caching and indexing to speed up page loads. If cache files are outdated, they may reference non-existent pages, causing 404 errors. | Stale cache showing removed pages. Incomplete or failed reindexing. | Flush the cache. Reindex data. |
| 5. Incorrect Store or Website Configuration | Magento allows multiple store views and websites. If base URLs are incorrect, store pages may return 404 errors. | Incorrect base URL settings. Improper store switching setup. | Go to Stores > Configuration > General > Web and ensure correct URLs. If using a custom domain, update the base URL. |
| 6. Missing or Moved CMS Pages | Magento’s CMS pages can be deleted or renamed, causing broken links. | Manually deleting essential pages. Changing page URLs without updating links. | Check Content > Pages for missing pages. Restore them or update internal links. |
| 7. Broken Category or Product Links | Magento generates URLs based on product and category settings. If these settings change, old links may stop working. | Disabling or deleting a category/product. Incorrect product catalog URL settings. | Ensure products and categories are enabled. Regenerate the sitemap to update URLs. |
5 Impact of Magento 404 Errors
1. Poor User Experience (UX)
When customers land on a 404 error page, they may leave the site instead of searching for the right product. It can:
-
Frustrate visitors and reduce trust in the store.
-
Increase bounce rate, leading to lower engagement.
-
Results in lost sales opportunities as users abandon the purchase process.
Example: A customer searching for "Men’s Running Shoes" clicks a link but lands on a 404 page. Instead of searching again, they leave and buy from a competitor.
2. SEO Ranking Drops
Google and other search engines penalize websites with frequent 404 errors.
-
Broken links reduce crawl efficiency, making indexing pages harder for search engines.
-
A high number of 404 errors lowers domain authority, impacting rankings.
-
Poor user signals like high bounce rate and low time on site affect SEO performance.
Example: Google detects multiple 404 errors in a Magento store. Over time, affected pages lose visibility in search results, leading to less organic traffic.
3. Decrease in Conversion Rates
404 errors prevent users from completing purchases, leading to lost revenue.
-
If a checkout page or product page is missing, customers cannot buy.
-
Internal links breaking can lead users to dead ends. It stops them from navigating further.
-
Customers may lose confidence in the site’s reliability and shop elsewhere.
Example: A Magento store owner removes an old product but forgets to set up a 301 redirect. Customers visiting the product page get a 404 error and leave without checking similar products.
4. Negative Impact on Site Performance
Too many 404 errors can slow down site performance.
-
Search engine crawlers waste time trying to access broken URLs instead of indexing new content.
-
Magento logs 404 errors, increasing server load and slowing down response times.
-
Frequent errors indicate a lack of site maintenance, affecting brand reputation.
Example: A Magento store with many deleted product pages but no redirects causes Google’s bots to waste resources on broken links. They are not able to rank new products.
5. Increased Customer Support Requests
Shoppers encountering 404 errors may contact customer support instead of finding products themselves.
-
Increases workload for support teams, reducing efficiency.
-
It can lead to customer frustration and poor brand perception.
-
Drives up operational costs due to unnecessary queries.
Example: A customer emails support asking why a category page is not working. Instead of self-service shopping, they rely on manual help, delaying purchases.
7 Best Practices to Prevent Magento 404 Errors
1. Keep URLs Consistent
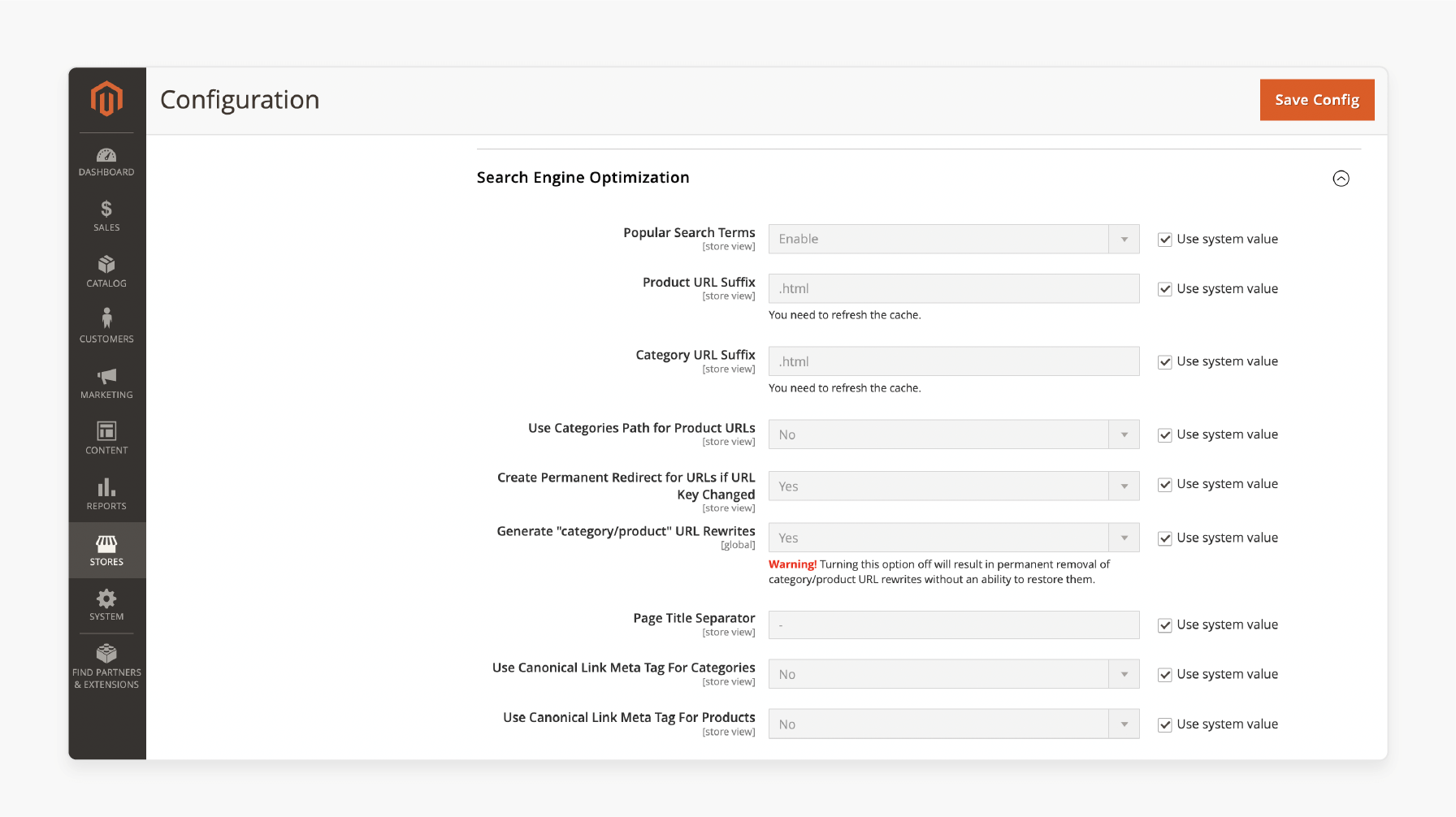
Changing URLs frequently can break links and cause 404 errors. To avoid this:
-
Avoid unnecessary URL changes once a product or category URL is set.
-
Magento allows automatic rewrites, but this can lead to duplicate URLs. You should disable automatic URL rewriting. Navigate to Stores > Configuration > Catalog > Catalog > Search Engine Optimization, and disable Use Categories Path for Product URLs if not needed.
-
Implement 301 redirects whenever necessary URL changes are made. It helps maintain search rankings and prevent broken links.
2. Use Proper Redirects
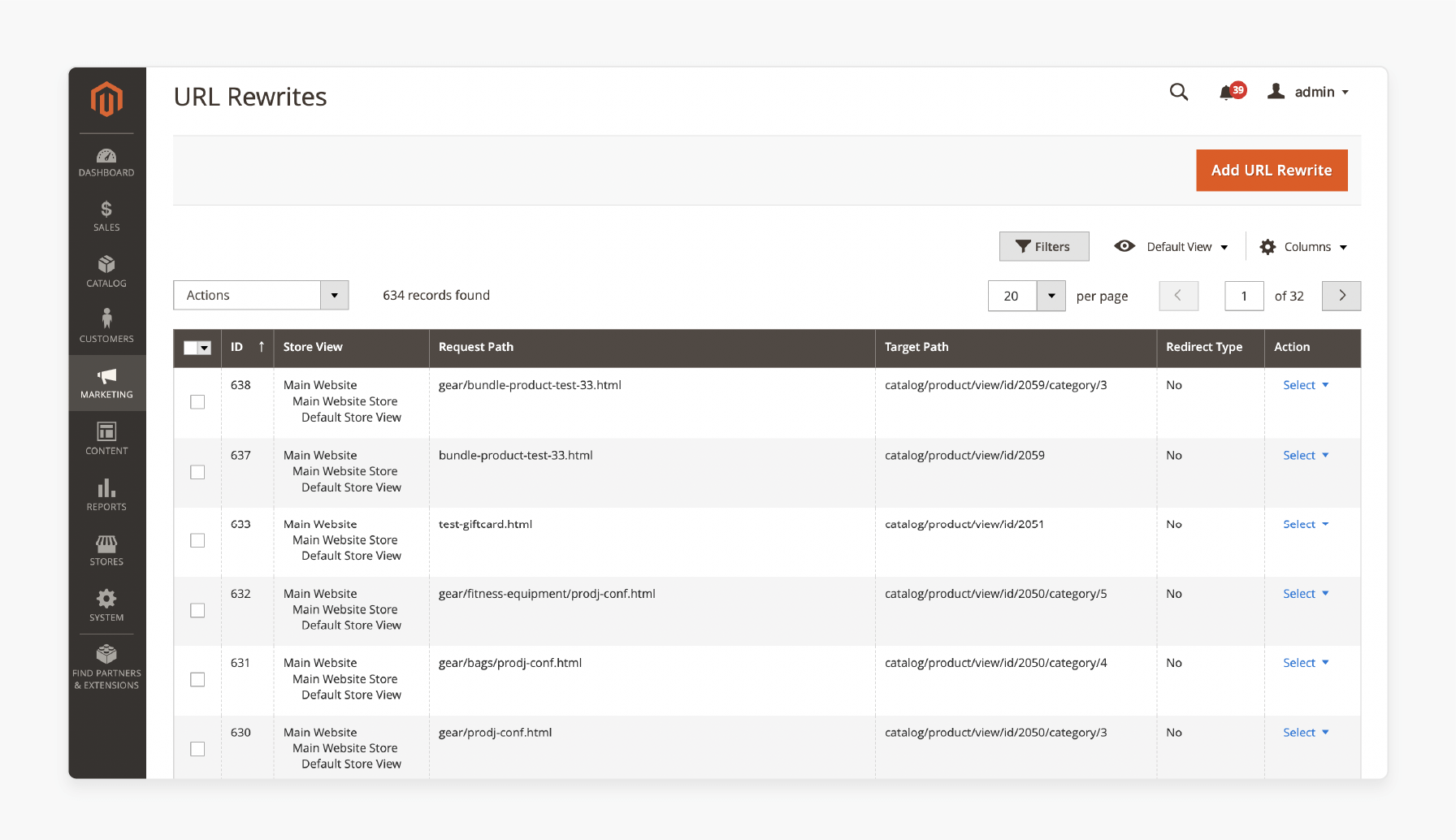
Redirects ensure users and search engines are guided to the correct pages instead of landing on a 404 error page.
-
Use 301 redirects for permanently removed or updated pages.
-
Magento’s built-in URL rewrite management helps set up redirects from Marketing > SEO & Search > URL Rewrites.
-
Avoid 302 redirects unless the change is temporary.
3. Refresh Cache and Indexes
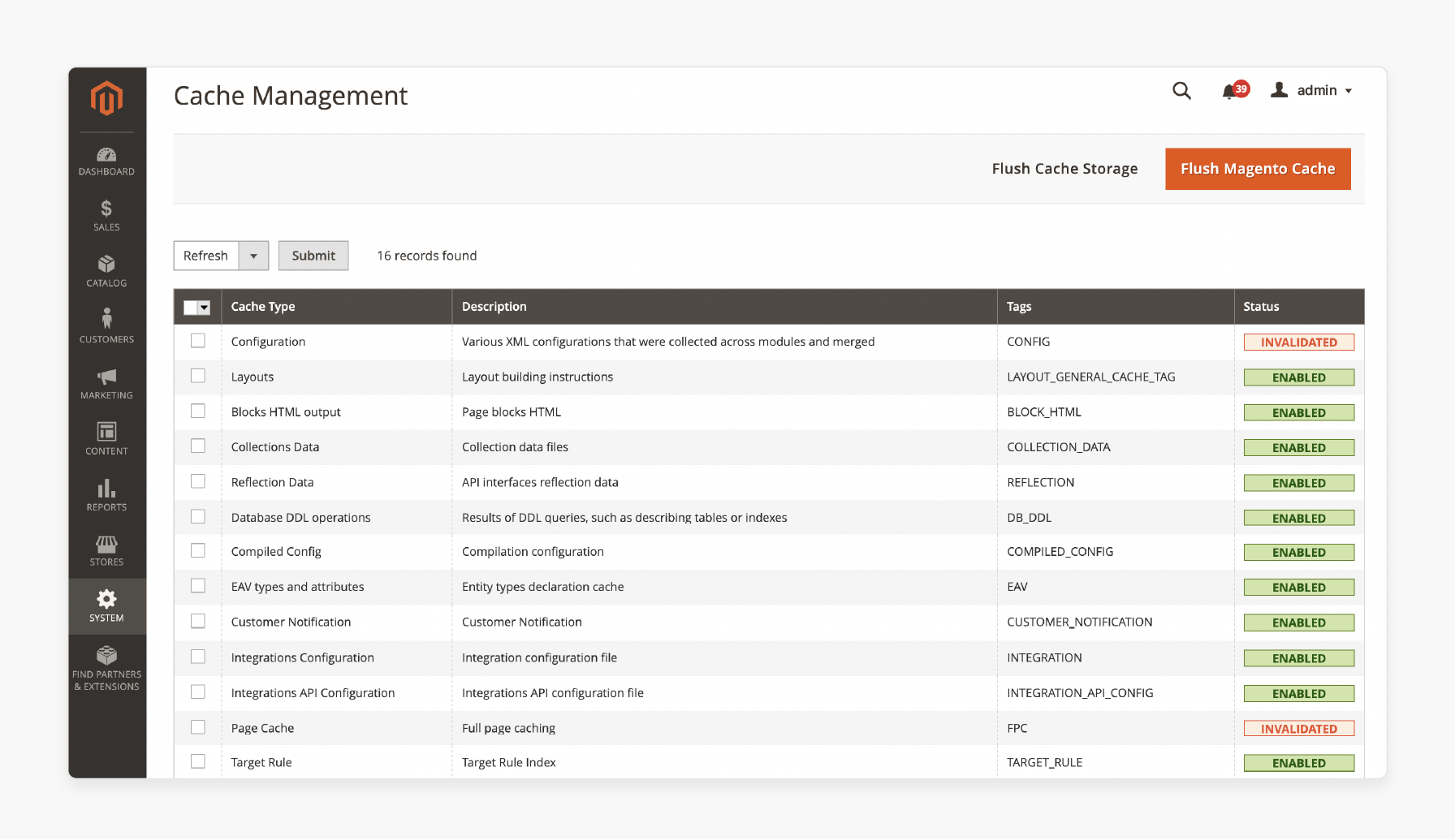
Magento uses caching and indexing to improve performance. Outdated cache files can cause 404 errors.
-
Clear Magento cache via Admin Panel > System > Cache Management or using the CLI command.
-
Reindex Magento to ensure all product and URL updates are reflected.
4. Check Permissions & File Paths
Incorrect file permissions can restrict access to pages and cause 404 errors.
-
Ensure proper file permissions.
-
Verify the .htaccess file settings to ensure no incorrect rules are blocking pages.
5. Fix Broken Links
Broken internal and external links can cause frequent 404 errors.
-
Use Google Search Console to check missing URLs.
-
Magento SEO audit tools like Screaming Frog and SEMrush can help detect broken links.
-
Manually check navigation menus and internal links after product/category updates.
6. Ensure Correct Store Configuration
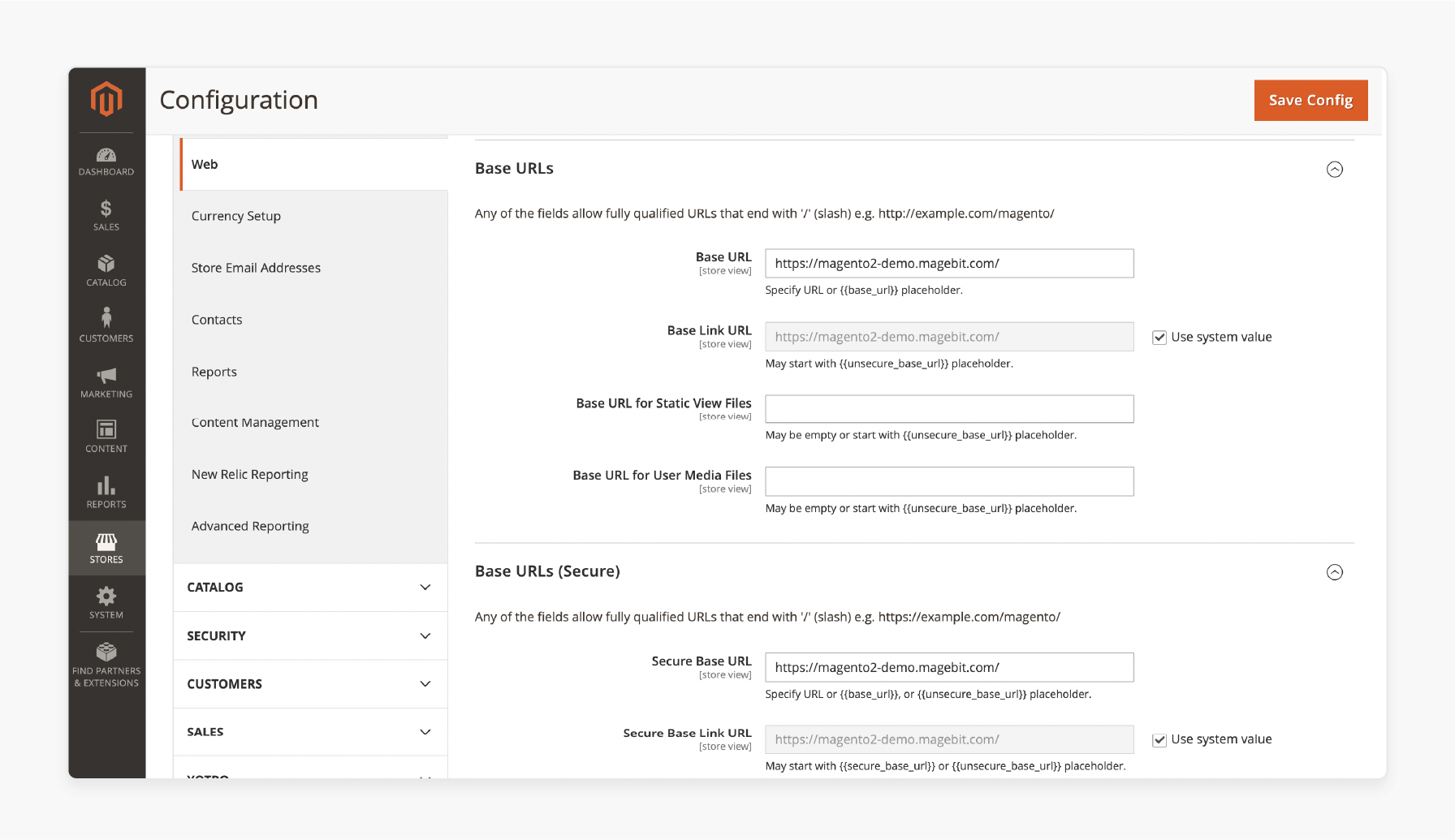
Incorrect Magento store settings can lead to broken URLs.
-
Check the base URL configuration under Stores > Configuration > Web. Ensure the Secure Base URL and Unsecure Base URL are set correctly.
-
If running multiple store views, verify that the Store View settings are assigned to the correct website.
7. Update & Maintain Extensions
Outdated or incompatible Magento extensions can cause missing pages.
-
Keep all extensions updated to avoid conflicts.
-
Disable extensions temporarily if a 404 error occurs after installation.
FAQs
1. How do I fix a 404 error in Magento?
To fix the 404 error in Magento, check URL settings, clear the cache, and update URL rewrites. If the 404 not found error occurs after installing a module, disable conflicting Magento 2 extensions via SSH. Ensure correct status code settings for proper redirects.
2. How can you customize the 404 error page not found in Magento?
You can customize 404 pages by editing the CMS error message in Magento’s admin panel. Navigate to Content > Pages, create a custom 404 page, and set it as default. It improves UX and SEO by guiding users to a relevant page instead of a dead-end.
3. Why am I getting a Magento admin 404 error after installing an extension?
A Magento admin 404 error after installing new Magento 2 extensions is usually due to missing permissions. Run php bin/magento setup:upgrade and cache:flush to fix the Magento admin 404. Ensure admin roles are properly assigned to avoid access issues.
4. How do you redirect a page with a 404 error to a new relevant page?
To redirect a page with a 404 error, use Magento’s URL rewrites or the Advanced SEO Suite extension. Set up a 301 redirect from the old 404 error page not found to a homepage or relevant page. It helps retain traffic and maintain Google Analytics tracking.
Summary
Magento 404 errors occur when requested webpages are unavailable, affecting customers and admin users. The article explores the types of errors, including:
-
Customers encounter frontend 404 errors when pages are deleted, or URLs are incorrect.
-
Admin panel 404 errors occur when Magento admins cannot access backend pages.
-
Storefront 404 errors occur if the Magento base URL is incorrect.
-
404 errors from custom modules occur when extensions interfere with store functionality.
Ensure a seamless shopping experience and avoid Magento 404 errors with managed Magento hosting.





