
3 Steps to Add New Magento 2 Tax Class
Want to ensure accurate tax calculations for every order? Magento 2 tax class settings help manage taxes across various products and customer groups and streamline checkout.
In this tutorial, we will explore the different types and configuration steps of the Magento 2 tax class.
Key Takeaways
-
Categorize products and customers for accurate tax calculation.
-
Configure tax rules by linking rates to specific products and customer types.
-
Step-by-step guidance to add new tax classes for products and customers.
-
Best practices keep tax settings organized, compliant, and updated.
-
Streamline tax setup for better store performance.
What is Magento 2 Tax Class?
Magento 2 tax class is a way to categorize products and customer groups for applying specific tax rates during checkout.
Magento offers two primary classes for tax, including:
-
Product Tax Class
-
Customer Tax Class
Product classes for tax allow you to assign tax rates to different types of products. These include taxable or non-taxable goods.
Customer classes for tax set tax rules based on customer types. These include retail or wholesale customers.
Configuring classes for tax ensures that the correct tax rate is automatically applied. It helps stores meet tax requirements and simplify tax management across diverse regions and product categories.
Different Types of Tax Classes in Magento 2
1. Product Tax Class
A product class for tax helps define which tax rate applies to each product type. It is essential for stores that offer various kinds of products. It is especially true when some items are taxable while others are exempt.
It lets you assign a specific tax rate based on the type of product being sold. It helps Magento automatically apply the appropriate tax at checkout. It also ensures accuracy and compliance with local regulations.
Examples:
-
Taxable Goods: These are most common for standard products that are subject to sales tax.
-
Non-taxable Goods: These are used for items exempt from tax. These include certain digital goods or exempted categories.
-
Gift Cards: Gift cards are a separate category used for non-taxable products.
2. Customer Tax Class
The customer class for tax allows store owners to create tax rules based on the type of customer. The flexibility helps businesses apply different tax treatments to different customer segments. It is useful in B2B scenarios or for wholesale and reseller customers.
Customer classes for tax customize tax rates for specific customer sets, such as retailers vs. wholesalers. The setup helps businesses that deal with both retail and wholesale clients. It enables the system to handle taxes automatically, depending on who is purchasing.
Examples:
- Retail Customer: It includes standard customers who are typically taxed at full rate.
- Wholesale Customer: It includes customers who are often eligible for tax exemptions or reduced tax rates.
- Reseller: They are typically exempt from sales tax if purchasing for resale.
How to Add New Tax Class in Magento 2?
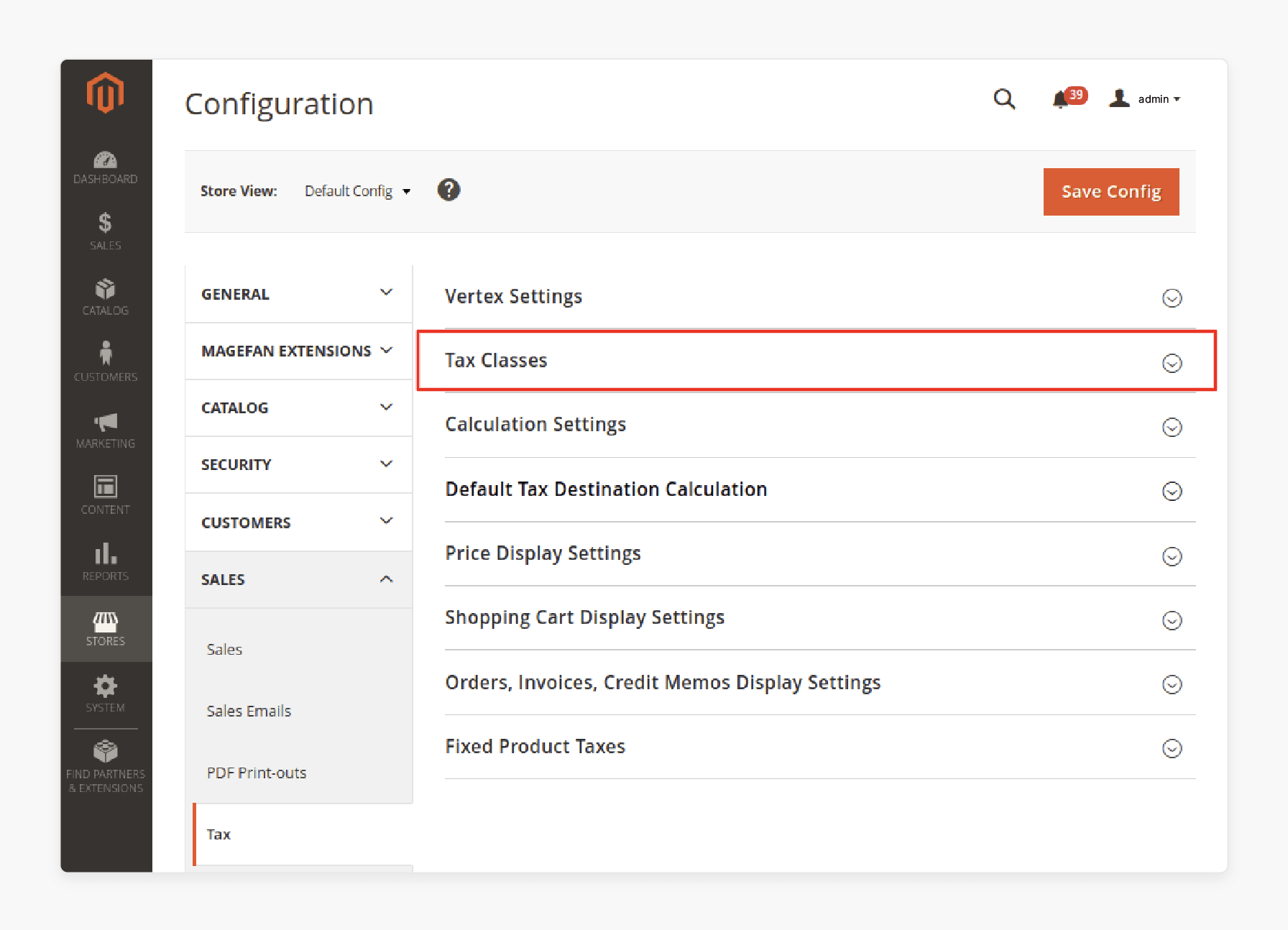
-
Go to Stores > Configuration > Sales > Tax.
-
Locate the Tax Classes section.
-
Add new tax classes for shipping and default tax classes for products. Options you can select from include:
-
Taxable Goods
-
Refund Adjustments
-
Gift Options
-
Order Gift Wrapping
-
Item Gift Wrapping
-
Printed Gift Card
-
Reward Points
-
You can assign different classes for tax to products directly when creating or editing them, except for the default class for tax in the configuration.
By default, Magento uses retail customers as the tax class for customers. You can create additional customer tax classes in your store and assign them to specific customer sets. Ensure each customer is categorized accordingly.
Note: You can add tax classes in Magento 2 when creating tax rules.
Difference Between Tax Class, Tax Rates, and Tax Rules in Magento 2
| Features | Tax Rules | Tax Class | Tax Rates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a way to categorize products and customers for tax purposes. It defines who or what will be taxed. | It is the percentage of tax applied based on location. These include city, state, region, or country. | A tax rule is the set of conditions that Magento uses to determine when and how to apply a specific tax rate to a product or customer. It combines tax classes and tax rates to create specific tax applications. |
| Purpose | It ensures that products and customers are grouped appropriately. It helps Magento know when and how to apply specific tax rates. | It defines the exact amount of tax to apply. It is according to the rules of each jurisdiction. | It links customer and product tax classes with tax rates. It helps determine when and how much tax to apply at checkout. |
| Examples | A retail customer purchasing a taxable product would have both the retail customer tax class and the taxable goods class assigned. It enables Magento to calculate tax on the transaction. | If a product is being shipped to California, the California State Tax Rate would apply. It ensures the correct regional tax is added to the order total. | A tax rule could state that for customers with the retail customer tax class purchasing items in the Taxable Goods Product Class in California, the California State Tax Rate applies. |
Best Practices for Managing Tax Classes in Magento 2
1. Define Tax Classes Clearly
-
You should establish clear distinctions between taxable and non-taxable products and different customer classes. These include:
-
Retail
-
Wholesale
-
Reseller
-
-
It ensures that each class has a distinct purpose and application.
-
Name classes for tax intuitively, like retail customers and taxable goods. It makes them easy to identify and assign. It helps minimize errors in setup and management.
2. Organize Tax Rates by Region
-
Set up tax rates according to location requirements like:
-
State
-
Country
-
Region
-
-
Assign each rate for tax to its corresponding region to ensure compliance. This is especially true if your business operates in multiple locations and has tax rates that vary.
-
Tax rates can change frequently. Review and update rates regularly to ensure your store complies with the latest compliance regulations.
3. Configure Tax Rules Correctly
-
Create tax rules that link specific product and customer classes for tax with applicable rates for tax.
-
The step ensures that only the correct combinations of product, customer, and rate are applied.
-
If certain customers are tax-exempt in specific regions. You should create specific rules to handle these scenarios separately. It helps prevent charging unnecessary taxes.
4. Test Tax Setup Thoroughly
-
Conduct test transactions with different products and customer types. It helps confirm that the correct tax is applied.
-
Testing helps identify any misconfigurations in tax rules or rates.
-
Ensure that your tax settings work for different checkout scenarios. These include shipping to multiple regions or applying discounts. These can impact the total tax amount.
5. Maintain Documentation
-
Keep a record of all tax configurations in use, including:
-
Classes
-
Rates
-
Rules
-
-
It helps easily troubleshoot any issues and track updates when tax regulations change.
-
Record when rates for tax or rules are updated or changed. It helps you stay compliant and allows others on your team to understand the setup.
6. Stay Updated on Regional Tax Laws
-
Tax regulations vary by region and can change frequently. Stay informed about these changes in tax laws to update your rates or classes accordingly. It helps avoid compliance issues.
-
Consider using tax calculation extensions that integrate with Magento 2. These automate tax updates based on location. It helps simplify tax management for businesses with complex tax needs.
7. Review Settings for New Products and Customer Groups
-
When adding new products, verify that the correct class for tax is assigned. It helps avoid accidentally charging incorrect rates.
-
Ensure that new customer sets (e.g., wholesale) receive appropriate tax class assignments. It helps avoid undercharging or overcharging tax.
8. Optimize for Performance
-
Avoid creating redundant or overlapping tax rules. These could slow down performance or cause tax calculation errors.
-
Keep your tax setup as straightforward as possible by consolidating classes for tax and rules where it makes sense. It reduces complexity and can improve store performance.
FAQs
1. How do I add a new tax rate in Magento 2?
Add new tax rate in Magento 2 by navigating to Stores > Taxes > Tax Zones and Rates. Set the rate by selecting the zone and entering the desired percentage. Save the Magento configuration to apply this new rate across relevant classes for tax.
2. Does Magento 2 class for tax affect product price?
The applied class for tax can impact product price in Magento 2. Depending on the class for tax assigned, Magento calculates tax according to the rate linked to the product. It ensures the correct amount is added at checkout.
3. What is the default tax destination in Magento 2?
The default tax destination in Magento 2 refers to the address Magento uses to calculate taxes if no other address is provided. It is typically configured in Sales > Settings. It ensures consistent tax calculations for all product price setups.
4. Can I set a fixed product tax rate for a specific zone?
Magento 2 allows you to set a fixed product rate for tax based on tax zone. Simply create a tax rule linking the product’s class for tax with the selected tax zone. It ensures accurate rate application for products in that region.
Summary
Magento 2 tax classes simplify tax applications by categorizing products and customer sets. The tutorial explores the key points of classes for tax, including:
-
Assigns rates for tax based on product type, covering taxable and non-taxable goods.
-
It applies different tax rates to customer types, such as retail and resellers.
-
Add and configure classes for products and customers in the admin panel.
-
Organize tax rates by region and test configurations to ensure accuracy.
Take control of your tax management with ease on managed Magento hosting designed for smooth performance.







